| VIRAL FAMILY | Orthomyxoviridae Includes 7 genera:1. Influenza A, B, C, D2. Isavirus3. Thogotovirus4. Quaranjavirus | RhabdoviridaeCONTAINS 3 GENERA1. Lyssavirus2. Ephemerovirus3. Vesiculovirus |
| Disease caused by | Influenza A causes Swine flu. | Rabies caused by rabies virus which is a Lyssavirus. |
| Body system affected | Respiratory system | Central nervous system |
| Morphology | Size: 80-120nm in diameter. Shape: spherical | 11-15kb in length. Helical |
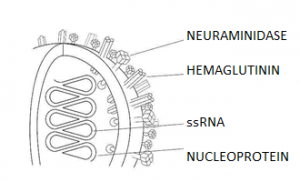
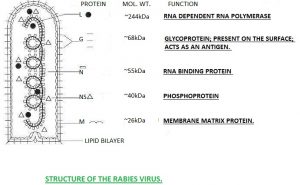
| Important proteins | HA (hemagluttinin) and NA (neuraminidase) | Five important protein, N (nucleo), P (phospho), M (matrix) G (glyco), L (large). |
| Genetics | RNA virusSingle strandAntisense or negative strand ssRNA.Segmented: 7 to 8 segments of RNA are there.Enveloped | RNA virusSingle strandAntisense or negative strand ssRNA.Non-Segmented, monopartite and enveloped. |
| Structure |
Segmented and spherical
|
|
| Incubation period | Highly variable; 30 to 90 days; can be 5 days or longer than 2 days.The incubation period is shorter in children than in adults.The virus travels 2mm per year towards the CNS; in children, it will take less time.If a person is a bit on the face or any place close to CNS, then incubation period will be short. | |
| Clinical symptoms | Sudden onset of fever, pneumonia, and cough. Most patients do not exhibit the full syndrome. | · Initial symptoms include fever, discomfort, and fatigue; these appear 2 to 10 days after the animal bite.· Acute symptoms include CNS dysfunction.· Dumb rabies: when paralysis predominates.· Furious rabies: when hydrophobia predominates. |
| Antigenic types | It has three antigenic types: type A, B, and C. type A and B can undergo variation; type C does not undergo variation. | Rabies virus and antigenically related rabies-like viruses. |
| Replication of the virus | · Virus binds or attaches to host cell by HA.· N-acetyl Neuraminic Acid is a cell membrane glycoprotein; it is the receptor for virus adsorption.· Viral HA binds to host N-acetyl Neuraminic Acid.· Virus moves into the cell as the endosome. Inside the endosome, the acidic environment dissolves the capsid.· Then the virion reaches the nucleus. · Then inside the host cell nucleus, viral transcription occurs.· Progeny virions collect in host cell cytoplasm.· Then they bud from the host cell.· Host cell dies in 6 hours. | · Virus attaches to host cell membrane by G-protein.· It penetrates the host cytoplasm by pinocytosis.· Uncoating of the virus.· RNA dependent RNA polymerase transcribes the other strand of the virus.· Then viral proteins are translated.· Replication of genomic RNA occurs with the help of proteins. Note that positive strand acts as a template for synthesis of the viral genome. |
| Pathogenesis and mode of infection.(Pathogenesis means the manner of development of disease). | · Respiratory secretions of infected persons.· The virus contains neuraminidase. NA acts on N-acetyl Neuraminic acid of the host cell; this causes liquefaction of N-acetyl Neuraminic acid.· The liquefied virion is able to travel deep into the respiratory tract.· The virus multiplies in the respiratory tract first of all.· Here it causes inflammation and edema. | · Exact pathogenic mechanism is not fully known.· The virus replicates in muscle tissue.· From here, it moves towards the CNS centrifugally. |
| Laboratory diagnosis | Study of antibody titer in the host body. | |
| Treatment | Drugs: Amantadine and Rimantadine.Takes 3 to 6 weeks to cure.Children of age group 5 to 9 are more affected. | |
| Preventive measures | Inactivated influenza viral Vaccines are developed every year. | |
| Epidemiology (incidence, distribution, and control of disease) | Occurs every year; generally in winter. Change in HA and NA protein types is responsible for the repeated epidemic and pandemic. |